Blockchains are distributed systems with unique and transparent data storage.Simply put, blockchain is a digital ledger, actually an electronic version of a paper ledger, and is in charge of recording transaction lists. In more detail, a blockchain is a sequential chain of different blocks that are linked together by cryptographic evidence.
The advent of blockchain technology created numerous advantages across a wide range of industries. First and foremost, blockchain is a technology for ensuring trust. However, the decentralised nature of blockchain also has a number of drawbacks. For example, unlike conventional centralised databases, blockchain is inefficient and requires large amounts of storage. Blockchain requires very high capacity to function, so it can take a considerable amount of time to create and validate new blocks.
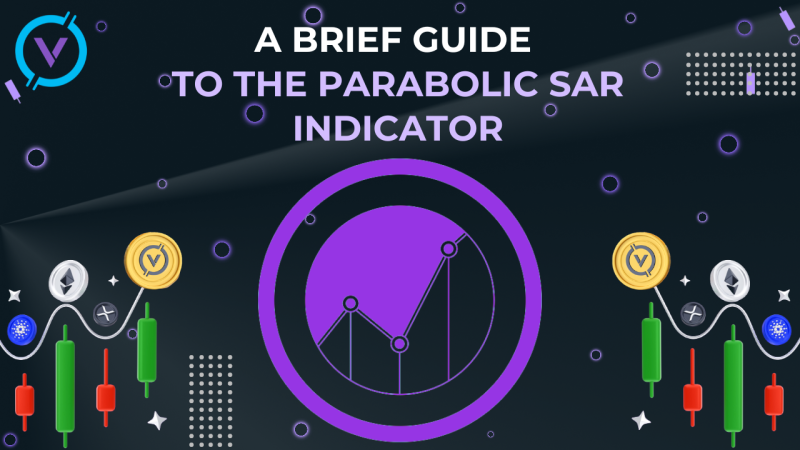
Advantages
1. Distributed network of nodes: most blockchains are distributed across hundreds of thousands of computers and each device holds a copy of the entire network. Hence maximum security and resilience to technical failures.
Each network node has the capacity to replicate and can store a copy of the database, due to this there is no single point of failure, which means that one node that is offline does not influence the network availability or safety. In comparison, many traditional databases run on one or more servers and are more prone to technical failures and the threat of cyberattacks.
2. Sustainable blockchain: undoing validated blocks is very unlikely, meaning that once the data has been registered on the blockchain, it is virtually impossible to delete or change it.
This means that blockchain technology makes it possible to store data on financial transactions, legal obligations and property rights, ensuring full transparency and universal accessibility for all to see, but also safeguarding against any hacking. Every change is monitored and constantly recorded in a distributed and public ledger.
For example, a company may apply blockchain technology to prevent fraud attempts among its employees. An example of an organisation using blockchain as a bill of lading is Alibaba, a transport company linked to the well-known Chinese sales service AliExpress. With this solution, Alibaba, its employees and subcontractors can track transport product flows and quantities in circulation online, but they cannot make changes to a specific register. This makes it much more difficult for an employee to hide suspicious transactions.
3. A reliable system: with traditional payment services, most transactions depend not only on both parties, but also on banks, credit card companies, etc.
But thanks to blockchain technology, there is no need for this anymore, because the distributed network of nodes performs transaction verification by means of mining. For this feature, blockchain is also known as a " trustless" system. Thanks to blockchain, systems built on trust have the potential to change or improve the way people make transactions. They no longer need to rely on untrusted institutions and third parties.
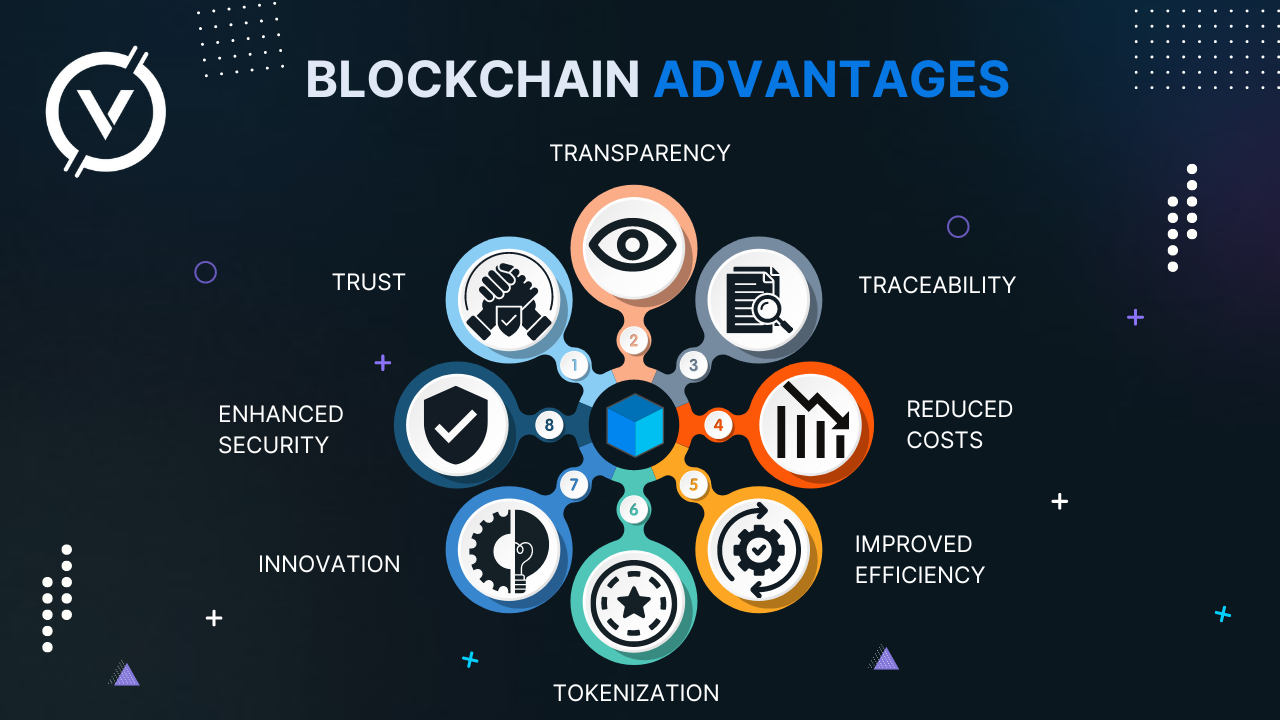
Disadvantages
1. 51% attack probability: the Proof-of-Work algorithm is effective in protecting blockchains and personal data from hackers, but it has a number of drawbacks. However, there are a number of possible attacks against blockchain networks.
For example, the "51% attack" or "double-spend attack". This blockchain attack involves a miner or group of miners attempting to spend their cryptocurrency twice on that blockchain. They attempt to produce a "double spend" - hence the name. A 51% attack occurs when 51% of a network's hashrate is managed by a single entity. This can be a mining pool or a single authority figure. One of the most famous examples was the Mt Gox attack in 2014, $450 million worth of bitcoins were stolen from one of the largest exchanges. After the updates, the attack is not possible.
As Bitcoin has risen in the marketplace, there are quite a few new miners in the system, eager to compete for the reward per block. For this reason, Bitcoin is a safe cryptocurrency. Miners have no incentive to invest large amounts of resources unless they act fairly and seek rewards per block.
In doing so, changing previously validated blocks as the chain grows becomes more complicated, as the communication between all blocks is done with cryptographic evidence. For the same reason, the more proof a block has, the higher the cost of changing or undoing transactions in it. Consequently, a successful attack would probably be able to change the transactions of the last few blocks within a short period of time.
2. Blockchain stability can also be a disadvantage: changing data or blockchain code is usually very difficult and often requires a hard fork.
Is a radical change in blockchain network protocol, resulting in the formation of two branches, one following the previous protocol and the other following the new version.
3. Private keys: blockchain uses asymmetric cryptography technology based on public or private keys to provide users with their ownership of their cryptocurrency units (or any other blockchain data).
Each blockchain address holds a related private key. The private key must be kept secret, although the address can be shared. To access their own funds, users need their private key. Theft or loss of a private key is tantamount to loss of access to the funds management and is virtually impossible to recover.
4. High energy consumption: blockchain, especially those using Proof of Work, is extremely inefficient. Miners waste a lot of effort and time because miners are competing for profit. Because every 10 minutes, on average, a block containing thousands of transactions is added to the blockchain.
If two miners create a valid block at about the same time, the winner will be the one who the network learns about first and adds another to his block, so that this blockchain becomes longer (and therefore more official). Therefore, there is always only one winner. To increase those odds and avoid the costs associated with single mining, miners typically join together in pools to pool their hash power, increasing the chances of block validation and ultimately sharing the mining if successful. Because of this, the amount of resources used by the Bitcoin network has increased considerably in recent times, and it now consumes more energy than many large countries..
5. A lot of storage is required: the size of the bitcoin blockchain is already around 200 gigabytes.
This is the maximum memory size for some personal laptops. If the ledger becomes very large for individuals to download and store it, the network runs the risk of losing nodes.
Final thoughts
Blockchain, despite its disadvantages, also has unique advantages and continues to evolve.It still has a long way to go before mass adoption, but in the future, companies and governments will experiment with new ways to use blockchain and try to capitalise on it. The technology is evolving and all the controversies will sooner or later be resolved.