The Internet is constantly developing. We have already met the past two generations Web 1.0 and 2.0, and we are eager to see what Web 3.0 will bring.
The Web 1.0 experience was static and lacked the ability to create our own sites with a rich variety of content as we do today. The Web 2.0 version made it possible to unite users through social networks and various sites, while making the sacrifice of decentralization.
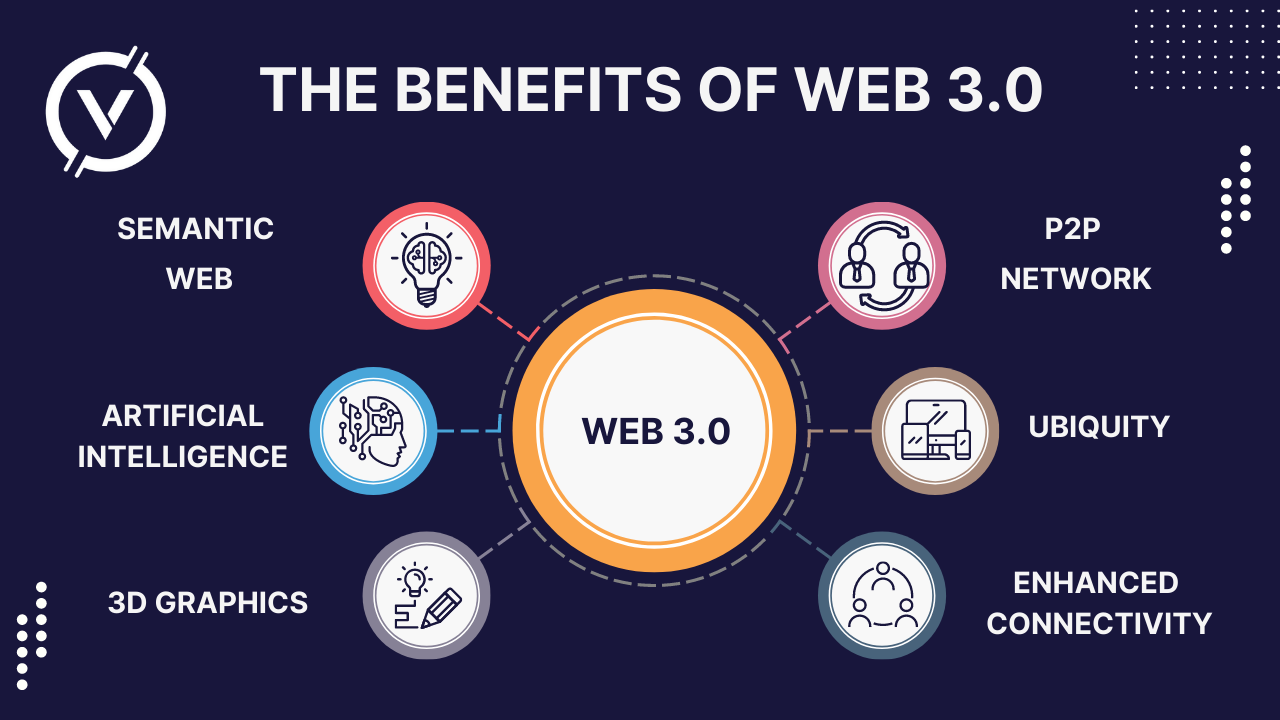
The concept of Web 3.0 promises to give full control over the information on the Internet, and to create a semantic network that allows programs to easily read and process user-generated content.
Blockchain technology will enable decentralization, free digital identification through cryptocurrencies, and an open digital economics.
The way users interact with the network promises to become more immersive with its 3D interface. In addition, users can expect easy content searching, relevant advertising and improved customer support. Some of the Web 3.0 technologies are already widely used in virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa, as well as in smart homes.
The Internet has changed a lot in the last twenty years. We have moved from Internet Relay Chat (IRC) to modern social networking platforms. Simple digital payments to complex online banking services. We have already experienced completely new Internet technologies, such as cryptocurrencies and blockchain.
The Internet has become an important element of human communication and continues to grow every year. We are familiar with Web 1.0 and 2.0, but what changes should we expect from Web 3.0? Let's explore in more detail what to expect.
What is Web 3.0?
Web 3.0 (or Web3) is the future generation of Internet technology, based primarily on machine learning, artificial intelligence (AI) and blockchain technology. The term was coined by Gavin Wood, founder of Polkadot and co-founder of Ethereum. Unlike Web 2.0, which concentrates on user-generated content stored on centralized Web sites, Web 3.0 gives users more control over their data online.
This concept is intended to create open, connected, intelligent websites and applications with advanced machine data analysis. Decentralization and the digital economy are also an important part of Web 3.0 because they give value to the content created online. It is also important to remember that Web 3.0 is a changing concept. There is no single interpretation, and its accurate meaning can vary depending on the definition.
How does Web 3.0 work?
Web 3.0 will provide personalized and relevant information faster by using artificial intelligence and advanced machine learning techniques. Smarter search algorithms and the development of Big Data analytics will allow machines to better understand user needs and recommend appropriate content. Web 3.0 will also center on protecting the ownership of content and supporting an open digital economy.
Modern websites such as forums or social networking sites most often contain static information or user-generated content. While this form allows information to be placed for a large number of people, it may not satisfy the needs of a particular user.A website should tailor the information it provides individually to each user, just as it does with real human interaction. In Web 2.0, as soon as information enters the Internet, users lose ownership and control.
I have a dream for the Web [in which computers] become capable of analyzing all the data on the Web – the content, links, and transactions between people and computers. A "Semantic Web," which makes this possible, has yet to emerge, but when it does, the day-to-day mechanisms of trade, bureaucracy, and our daily lives will be handled by machines talking to machines.
Berners-Lee and Gavin Wood have put their ideas together to make vast amounts of decentralized information more accessible to sites and applications. They will analyze and apply this information to ensure that it meets the needs of specific users. Blockchain serves as a tool for fair management of identity, data and property rights on the Internet.
The History of the World Wide Web
To better understand Web 3.0, Let's take a look at what we're doing now and what we've been able to do. In two decades we have already experienced huge changes:
Web 1.0
The first Internet network was built on what is now called Web 1.0 The term appeared in 1999 thanks to author and web designer Darcy DiNucci, who distinguished between Web 1.0 and Web 2.0. In the early 1990s, Web sites were built with static HTML pages that could only display information while users had no way to change or add new data. Social communication was limited only to simple chat rooms and forums.
Web 2.0
In the late 1990s, the move to a more interactive Internet began. Web 2.0 allowed users to interact with Web sites through databases, server-side processing, forms and the use of social media. These tools transformed the web experience from static to dynamic.
Web 2.0 has increasingly begun to focus on user-generated content, as well as the interaction between various sites and applications. Web 2.0 offered not just passive content consumption, but engagement in content creation. Most websites switched to Web 2.0 in the second half of the 2000s, and major technology companies had begun building social networks and cloud-based services.
The future and Web 3.0
The evolution of the semantically intelligent web becomes clear when we look at the history of the Internet. At first, data was presented to users in a static form. Users can then work with this data in a dynamic way. This allowed algorithms to create a more personalized and convenient online experience. Just look at YouTube or Netflix, and you can see how algorithms have improved those platforms and the user experience.
It is still unknown what the Web 3.0 version will be, but it could use peer-to-peer (P2P), blockchain, open source software, virtual reality, the Internet of Things (IoT) etc. With Web 3.0, the Internet will become more open and decentralized. Under the current system, users entrust access to their personal data and information to network and cellular providers. Perhaps with the arrival of distributed ledger technology, the situation will change and users will have a chance to regain ownership of their data.

The table lists the main differences between Web 1.0, 2.0 and 3.0:
|
Web 1.0 |
Web 2.0 |
Web 3.0 |
|
|
Content |
Passive participation for the users |
Platforms for communities and customer-generated content |
Ownership rights of the user for content creators |
|
Technologies |
HTML |
Dynamic HTML, Javascript, |
Blockchain, AI, machine learning |
|
Virtual environments |
None |
Some basic 3D use |
3D, VR, AR |
|
Advertising |
Obtrusive (banners, etc.) |
Interactive |
Targets based on user behavior |
|
Data storage |
Stored on the servers of individual websites |
Owned by major technology companies |
Allocated to users |
|
Audience |
Individual users |
Special user communities |
Interconnected users across different platforms and devices |
Key Features of Web 3.0
Web 3.0 is still far from being fully accepted, but its core concepts have largely been decided. The following describes the four most important factors of the Web 3.0 of the future.
Semantic markup
Programs are getting better and better at recognizing user data and content every year. But, as it is, there is still a long way to go before a deep understanding of semantics. For example, the use of the word "bad" could mean "good" depending on the context. This can be incredibly difficult for a machine to understand. However, by using Big Data and large amounts of information to study, AI is beginning to intuitively understand users' communication on the Internet, and better understand what users are writing.
Blockchain and cryptocurrencies
Data ownership, the online economics, and decentralization are critical aspects of Web3's future according to Gavin-Wood to achieve which will use a reliable, proven and tested blockchain system to achieve many of these goals. The tokenization of assets, the transfer of information down the chain, and the creation of digital identifiers is a huge innovation that is relevant to Web 3.0.
3D visualization and interactivity
Simply put, the Internet's look and feel will change radically. Already now we are seeing a move to a 3D environment that even includes virtual reality. The metaverse is one of the areas where such possibilities first appeared, and we are already communicating in 3D video games. The UI and UX fields are also working to make information more intuitive and accessible to users.
Artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence is the property of an intelligent system to perform those functions and tasks that are usually characteristic of intelligent beings. Bots already in use for customer service are just the first step to the future. AI can not only provide us with data, but also sort it. Most importantly, AI will then self-train and improve itself, which will reduce the amount of work required for human development.
What are the main advantages of Web 3.0?
The sum of the main features of Web 3.0 allows you to get a lot of benefits, but do not forget that they will all be highly dependent on the effectiveness of the underlying technology:
- No central control point. Because there are no intermediaries, no third parties can control user data. The lack of freedom reduces the likelihood of censorship by governments or corporations and decreases the activity of denial-of-service (DoS) attacks.
- The growing degree of interconnectedness of information. Because more products are connected to the Internet, datasets give algorithms a wide variety of information to analyze. This will allow them to understand how to provide more accurate information that meets the needs of every single user.
- More efficient browsing. With conventional search engines, finding the most relevant information was sometimes quite difficult.Over time, however, it has become easier for them to find semantically relevant results according to search context and metadata. This leads to a better browsing experience, which helps anyone find the information they want with ease.
- Improving advertising and marketing. When a user has a lot of ads popping up on the Internet of course it is very annoying. But if the ads meet your needs, they can be very useful rather than annoying. Web 3.0 seeks to improve advertising by using artificial intelligence systems and targeting with consumer data.
- Improved customer service. With regard to websites and applications, customer service is essential to the user experience. However, because of the high costs, many successful web services try to scale their customer service operations. They use smarter chatbots that can communicate with multiple customers simultaneously, users can have a superior experience with support agents.
How does cryptocurrency fit into the Web 3.0 concept?
Looking at Web 3.0, the potential of blockchain and cryptocurrencies is enormous. Decentralized networks create the motivation for more reliable and secure data ownership, governance and content management. Some of its most important sides for Web 3.0 are:
- Digital cryptocurrencies. Each user can create a wallet, which allows him to make transactions and plays the role of digital identity. This eliminates the necessity of storing data or creating an account with a centralized service vendor. The user has full control of his wallet, and the same wallet may often be used on more than one blockchain.
- Decentralization. With blockchain, it is easy to distribute information and power to a huge number of people. Unlike Web 2.0, where big tech giants dominate much of our online life.
- Digital Economy. By being able to own data on a blockchain and make decentralized transactions, a new digital economy is forming. This makes it easy to use and trade goods, services, and content online without having to specify bank or personal information. With this transparency, access to financial services improves and users begin to earn money.
- Compatibility. DApps and blockchain data are becoming more and more interoperable. Blockchains based on the Ethereum virtual machine can easily support DApps, wallets, and tokens, increasing the ubiquity required to create a connected Web 3.0.
Using Web 3.0
Although the Web 3.0 generation is still under development, we have a few examples of how to use its features:
Smart Homes.
One of the key features of Web 3.0 is ubiquity. Thus, data and online services are accessible through many devices. You can now automatically configure systems that control heating, air conditioning and other utilities in your home. This is done with smart and connected devices. The smart home also knows when you leave, when you come back, and what room temperature you prefer. It can use this and other details to create a different experience for you. You can run this system from your phone or other online device, no matter where you are.
Siri and Alexa virtual assistants.
Apple's Siri and Amazon's Alexa virtual assistants answer many Web 3.0 needs.
AI and live speech processing allow these services to better understand human speech commands. As a rule, the more people use Siri and Alexa, the faster their artificial intelligence and interactive capabilities improve. These assistants are a prime example of a semantically intelligent Web application of the Web 3.0 era.
Summary
The Internet went through significant changes since its inception, and it certainly continues to change and improve. As the amount of data available grows, websites and applications are increasingly running on a network that features improved characteristics for users around the world. Of course, there is no single concept of Web 3.0 yet, but innovations are beginning to enter our lives. It is becoming clear what technologies are expected in the future, and blockchain will certainly be the most important stage in their future Web 3.0 development.